- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
HFSS15: Arrays
Arrays
HFSS permits you to assign a virtual array based on a unit cell object. For driven Modal and driven Terminal designs, you can then simulate the array model using distributed processing, treating the instances as parent and child objects. This permits faster definition, display, and simulation of array based designs, such as antenna arrays. You can plot and animate array fields on cutplanes, lines or points. Post processing lets you view fields on any virtual instance.
The unit cells for an array can be rectangular, parallelogram, or hexagonal. You can define the required master and slave boundaries so as to create offset arrays. You can only edit the settings in the physical cell and these settings will be applied to the corresponding instances in the virtual cells.
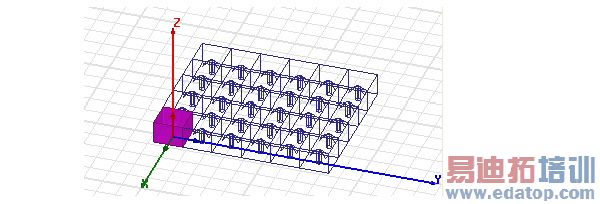
Once you have defined an array, you can designate any cell in the array as active or passive, or as padding. You can use the padding cell designation to define arbitrarily irregular arrays. Cells designated as padding are treated as background material for fields calculations.
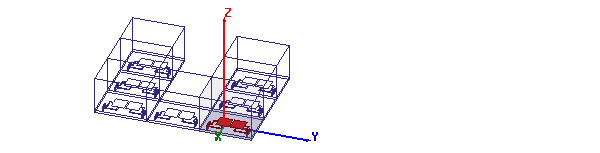
Most boundaries and excitations defined in the physical unit cell will have their corresponding instances in each virtual cell. The exception is incident wave, which is applied across the whole model and should include the 'expanded' model based on the array setup.
The basic process flow for using Create Array is:
1. Draw the unit cell, containing all appropriate boundaries and source definitions.
2. Create the antenna array, including name, dimensions, master and slave boundaries where needed for conformal meshing, and selection of row and column master/slave pairs for implicit definition of lattice propagation vectors. Designate which cells are active, passive, and padding.
3. Setup the distributed processor pool. Designs with arrays require HPC licenses.
4. Provide a memory statistic for the amount of RAM guaranteed on each DSO processor.
In the Setup, Enable Solver Domains is disabled because an array solve uses UI defined domains, not solver defined domains. Given a valid configuration, an Array solve can use a distributed memory solution.
The UI will provide the antenna array definition to the domain manager. This will cause the following to occur:
1. Instantiation of domains to represent the cells of the antenna array plus surrounding air padding cells.
2. Creation of internal domain manager data structures that are needed to support the solve and post processing. This includes appropriate domain parent/child relationships, transformations from the physical domain, interface information per pair of domains, and support for locating a domain by row/column coordinates within the antenna array.
For linking to Designer, the network data from HFSS will include both physical and virtual cells. This applies to both port locations and push excitations.
For Optimetrics solution quantities of both virtual and physical cells can be used for calculation.
For 2D Reports for models with Arrays, matrix solution quantities of virtual cells will be expanded into a vector in the same fashion as without the array. The entries are listed according to their [row, column] order in the corresponding "expanded" matrix.
For Port Field Display there is no GUI change. Only physical ports/terminals will be listed. There is no need to support visualization of user-selected cell (like field overlay plot) because the field patterns of the virtual modes are the same as those in the physical cells.
For designs with an Array, the Edit Sources dialog listing order will be as follows: Sources will be listed according to their cell [row, column] order in the array. For each cell, port/terminals are listed in creation/assignment order with mode in each port listed sequentially. Other type of sources, such as incident waves, will be listed after ports/terminals.
There will be no change in the far/near field pattern setup and far/near fields will be computed from radiation surfaces on all cells (both physical and virtual).
Copy/Paste design will copy an array. Copy/Paste geometry will NOT copy an array.
HFSS 学习培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您全面系统地学习掌握HFSS
上一篇:Assigning Color to Objects
下一篇:Assigning Coordinates to New Objects


