- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
HFSS15: Floquet Port: Mode Setup
In general Floquet modes are specified by two modal indices and a polarization setting. These designations resemble the textbook notation for rectangular waveguide modes, such as ``TE10.''
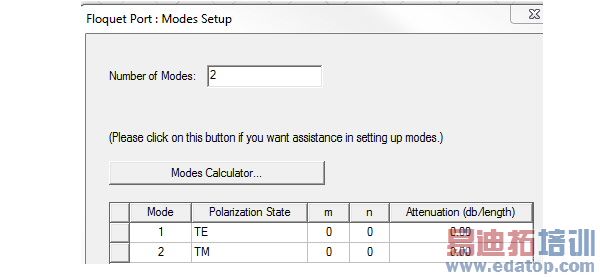
The default mode table specifies a pair of Floquet modes. The default modes both have modal indices equal to zero and are sometimes called "specular" modes, which are always an essential part of the Floquet mode set. For general frequency and scan conditions, other higher-order Floquet modes will be needed. A modes calculator, invoked by selecting the Modes Calculator button, is available to set these up for the user.
The values under Attenuation represent the modal loss in amplitude along the direction normal to the Floquet port plane. The numbers in this column are computed by the modes calculator that will help you decide which modes to keep.
Attenuation for a mode is a function of both the frequency and the scan angle specified in the modes calculator. When the latter includes more than one scan direction, the least amount of attenuation experienced by the mode over all the specified scan directions.
Thus when the table gives a value of 0 dB, at one or more scan directions specified in the modes calculator the particular mode propagates without attenuation. Similarly, when the table displays say 60 dB, a 60 dB per unit length is the least amount of attenuation at all specified scan directions. At any given direction, only the same or larger attenuations (for example, 70 dB per length) will occur. To improve simulation efficiency and interpret the results easily eliminate any modes that are not necessary. Do this by editing the Number of Nodes field in the Modes Setup tab.
Note: The list is trimmed from the bottom.
To change the order of items in the final Modes list, drag each corresponding line by the square box at the left of each row.
HFSS 学习培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您全面系统地学习掌握HFSS
上一篇:Firewall Configuration
下一篇:Four: Removing Small Features


