- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
HFSS15: Hertzian-Dipole Wave
An incident Hertzian-Dipole wave can be specified as either an Electric dipole or a Magnetic dipole. The Electric dipole simulates the field of an elementary short dipole antenna placed at the origin. The Magnetic dipole is useful for EMC/EMI applications. Specify a Hertzian dipole as follows:
Cartesian Coordinates
1. Click HFSS>Excitations>Assign>Incident Wave>Hertzian-Dipole Wave.
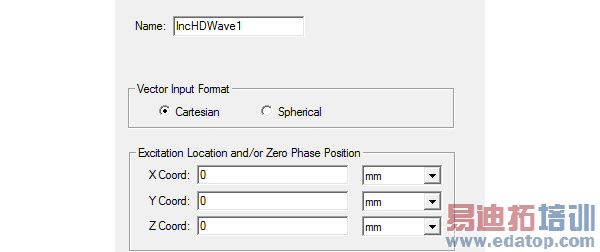
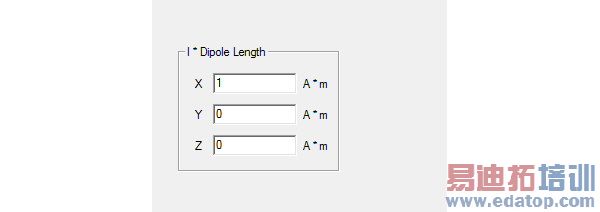
2. Select Cartesian and click Next, the subsequent dialog lets you define the dipole length.
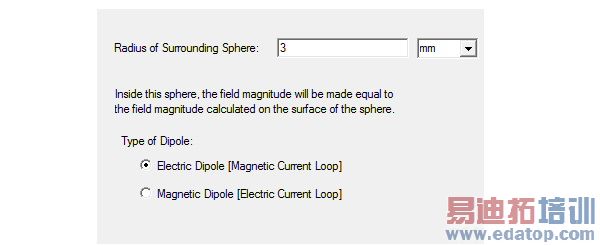
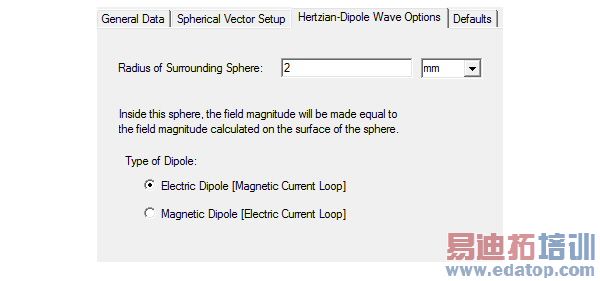
3. Define the types of dipole and the radius in the Hertzian-Dipole Wave Options dialog box.
Spherical Coordinates
1. Bring up the Incident Wave Source dialog box for a Hertzian dipole and select Spherical.
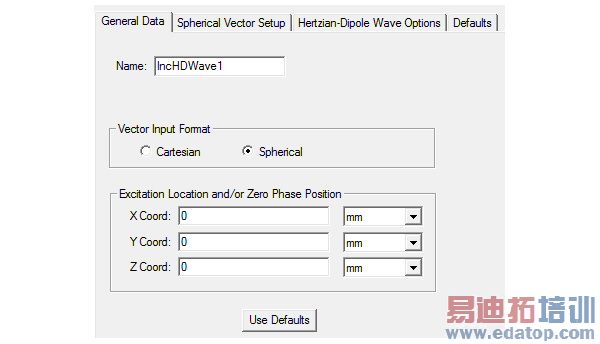
2. Enter the X-, Y-, and Z-coordinates of the Excitation Location and/or Zero Phase Position (the origin for the incident wave).
3. A sample setup for the IWavePhi, IWaveTheta, and I*Dipole Length is shown below.
Note: I is the current amplitude (peak value).
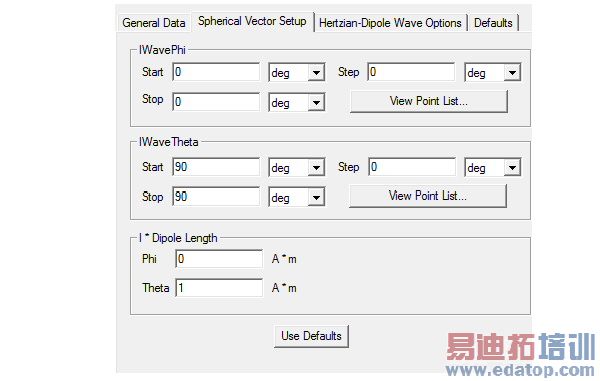
A spherical grid is created when q is swept through each f point. At each grid point, an incident wave is present traveling towards the origin of the coordinate system for the design. The number of incident waves and grid points can be calculated by multiplying the number of f points by the q points.
Note: Only a single incident wave angle can be defined for periodic structures which are defined with master and slave boundaries.
4. Set the Hertzian-Dipole Wave options and then, click Finish.
The incident wave you defined is added to the Excitations list in the Project.


