- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
HFSS15: Specifying Initial Mesh Settings
You can specify the initial mesh settings, including the surface approximation and the meshing approach. Initial Mesh Settings tapply to all objects; however, if you apply separate surface approximation mesh operations to specific objects, the object settings take precedence over the general setting.
For most designs, you can let HFSS automatically choose which of two meshing approaches to take. HFSS predicts which one gives the best results, balancing mesh reliability, speed, quality, size and design characteristics. In most cases, HFSS uses Ansoft TAU mesh, rather than the Ansoft classic mesh. In general, it looks for specific features (for example, stacks of large planar parallel facets with small gaps) and situations where the initial Ansoft Tau mesh is 4 times larger than the Ansoft Classic. In a few cases, you may decide to override the automatic choice and designate the mesher to use. To do so:
1. Select HFSS>Mesh Operations>Initial Mesh Settings... or in the Project tree, right-click on Mesh Operations, and select Initial Mesh Settings from the shortcut menu.
The Initial Mesh Settings dialog appears with the Surface Approximation tab selected.
2. Under Maximum Surface Deviation, do one of the following:
• Select Ignore if you do not want to use surface deviation settings for the selected faces.
• Select Set maximum surface deviation (length), and then type the distance between the true surfaces of the selected faces and the meshed faces in the text box.

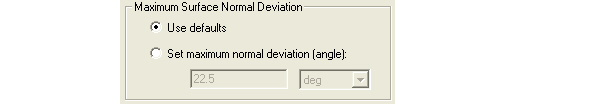
3. Under Maximum Surface Normal Deviation, do one of the following:
• Select Use defaults if you want to use HFSS’s default normal deviation setting for the selected faces, which is 22.5 degrees.
• Select Set maximum normal deviation (angle), and then type the angular distance between the normal of the true surface and the corresponding mesh surface in the text box.
4. Under Maximum Aspect Ratio, do one of the following:
• Select Use defaults if you want to use HFSS’s default aspect ratio settings for the selected faces, which are 10 for curved surfaces and 200 for planar surfaces.
• Select Set aspect ratio, and then type a value in the text box. This value determines the shape of the triangles. The higher the value, the thinner the triangles. Values close to 1 will result in well-formed, wide triangles.
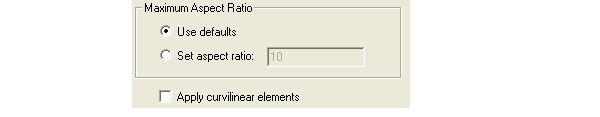
5. You can also uncheck or check Apply curvilinear elements. For models with curved surfaces, this increases accuracy, though it costs more memory. In some situations, you may choose to uncheck the setting. See Rectilinear Elements and Curvilinear Elements.
6. To make your choice the default, use the Save as default checkbox.
7. Select to the Meshing Method tab.
It contains radio buttons for:
• Auto (the default)-- HFSS automatically selects the mesher. In most cases, this will be Ansoft TAU mesh.
• Ansoft TAU Mesh--this includes Surface representation choices for Strict or Tolerant. Strict performs stitching, resolves surfaces and contacts more accurately, but takes more time and may cause issues for dirty models. Tolerant uses a looser tolerance for surface representation, which may be better for dirty or very complex geometry.
• Ansoft Classic Mesh--this is based on the HFSS 11 mesher.
8. To make your choice the default, use the Save as default checkbox.
9. Click OK to apply your choices.
The settings will be applied to the initial mesh generated.
HFSS 学习培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您全面系统地学习掌握HFSS
上一篇:Specifying a Single Goal Value
下一篇:Solving a Single Setup


