- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
HFSS15: Terminals Theory
HFSS can categorize microwave structures in terms of a black-box that relates voltages and currents flowing in and out of a given structure. The black-box has several terminals, each with an associated voltage/current pair. In HFSS, these terminals reside inside wave ports that enable post processing of a modal representation of the black-box into the terminal representation.
When a terminal project is solved using HFSS, the number of modes for a port is determined by the number of terminals touching the port. If N+1 distinct conductors touch the port, there are N terminals and one reference conductor usually referred to as ground. The modal port representations of the electric and magnetic fields are:
| 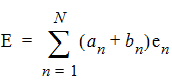
| (1) |
| 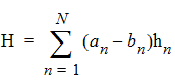
| (2) |
where an and bn are unitless complex amplitudes of the ingoing and outgoing modal fields, respectively. The modal black-box representation of a given structure is given by HFSS in terms of the generalized scattering matrix, S,
|
| (3) |
where a and b are the unitless complex modal coefficient vectors. In order to obtain a terminal representation of the black-box, N integration paths Ci and N integration loops Li are used to define N voltages and N currents, respectively,
| 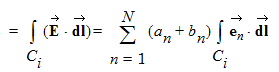
| (4) |
| 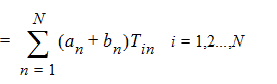
|
|
| 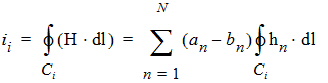
| (5) |
| 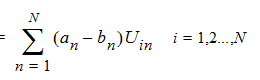
|
|
In matrix notation, the equations become
|
| (6) |
|
| (7) |
Combining these equations with (3), yields the following circuit or terminal description of the black-box representation of the structure
|
| (8) |
where the terminal admittance matrix Y is given by
|
| (9) |
In HFSS, a generalized terminal scattering matrix St is supplied to the user..
|
| (10) |
where a and b are ingoing and outgoing pseudo waves, respectively. The St ![]() matrix is obtained by assuming that the voltages and currents are measured by some device with a given renormalizing impedance. This assumption leads to the following relations.
matrix is obtained by assuming that the voltages and currents are measured by some device with a given renormalizing impedance. This assumption leads to the following relations.
|
| (11) |
|
| (12) |
where Zref is a renormalizing impedance matrix representing the measuring device. In HFSS, the user has the option to use the terminal characteristic impedance matrix, Zo, as the renormalizing impedance matrix by using the 'Do Not Renormalize' option in the port post processing tab. This means that the measuring device is perfectly matched to the transmission line. By default, all the terminals are individually renormalized which results in Zref being a diagonal renormalizing impedance matrix. An expression for St is obtained by using equations (8) - (12)
|
| (13) |
Terminals in HFSS can also be used to create differential pairs as discussed in the Differential Pairs section.


