- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
Salisbury Screen的入射波与分析设置
我最近一个多月开始自学电磁学与HFSS,学姐给我布置了一个关于Salisbury Screen的仿真任务,在HFSS仿真中遇到几个困惑想要请各位前辈指导一下。
原题:一个Salisbury Screen吸收体,如果它的介质基底的厚度t=10mm,介电常数为2.65,损耗角常数忽略,请问在电磁波垂直入射的情况下,它的带宽(反射系数小于-10dB)为多少?
以下是困惑: 1.电磁波源距离吸收体的距离对仿真结果是否会有影响?
2.电磁波设置里的k为传播方向,那应该在x,y,z三个方向各有两个小方向,只用选择1或-1,为什么可以输入任意数字?我按照途中所示设置是否合理?
3.因为Salisbury Screen是在基板前1/4个波长放置一个电阻层,而此前在仿真贴片天线时电阻层选用Perfect E,这次依然采用Perfect E是否合理?如果合理,那么ground边界条件设置也是Perfect E,两个面是否意味着可以互相转化?
4.题目要求仿真得出带宽大小,但在这个仿真中,我一直摸索不到测出带宽的方法,请问在仿真时如何设置可以查看线路带宽?
不小心误发了两次,麻烦版主帮忙删除一下
你应该先理解物理上的原理,运气好有一篇中文的
Design of multiband Salisbury screen based on high impedance surfaces.pdf
======================================================================
Salisbury screens operate on the same principle as optical antireflection coatings used on the surface of camera lenses and glasses to prevent them from reflecting light. The easiest to understand Salisbury screen design consists of three layers: a ground plane which is the metallic surface that needs to be concealed, a lossless dielectric of a precise thickness (a quarter of the wavelength of the radar wave to be absorbed), and a thin glossy screen.
1.When the radar wave strikes the front surface of the dielectric, it is split into two waves.
2.One wave is reflected from the glossy surface screen. The second wave passes into the dielectric layer, is reflected from the metal surface, and passes back out of the dielectric into the air.
3.The extra distance the second wave travels causes it to be 180° out of phase with the first wave by the time it emerges from the dielectric surface
4.When the second wave reaches the surface, the two waves combine and cancel each other out due to the phenomenon of interference. Therefore, there is no wave energy reflected back to the radar receiver.
To understand the cancellation of the waves requires an understanding of the concept of interference. When two electromagnetic waves that are coherent and are traveling in the same space interact, they combine to form a single resultant wave. If the two waves are "in phase" so their peaks coincide, they add, and the output intensity is the sum of the two waves' intensities. However, if the two waves are a half-wavelength "out of phase", so the positive peaks of one wave coincide with the negative peaks of the other, the two waves subtract, and the difference is zero.
The thickness of the dielectric is made equal to a quarter of the wavelength (λ/4) of the expected radar wave. Since the second wave (in step 2.) travels the thickness of the dielectric twice (once going in and once coming out), the extra distance it travels is a half-wavelength (λ/2). So it is a half wavelength out of phase with the first wave when they combine, and the two waves cancel.
=========================================================================================
这应该是仿真个吸波材料的吸收频段,它的带宽也就是能吸收电磁波的那段带宽了吧
Salisbury屏的优化设计.pdf
在百度上随便找了篇,可以参考下,这个写的比较概括,可以去找找相关的硕士论文
谢谢,这篇文章也是我看的第一篇文献。只是因为这次的HFSS仿真和我之前做过的几个并不相同,所以在软件的功能方面遇到了挺多的困惑。
非常感谢,只是我最近也读了很多关于Salisbury屏的相关文章,对它的物理原理也算是有一定的认识。但是因为我才接触HFSS软件并不是很久,所以在仿真时遇到了很多困难不能自行解决。
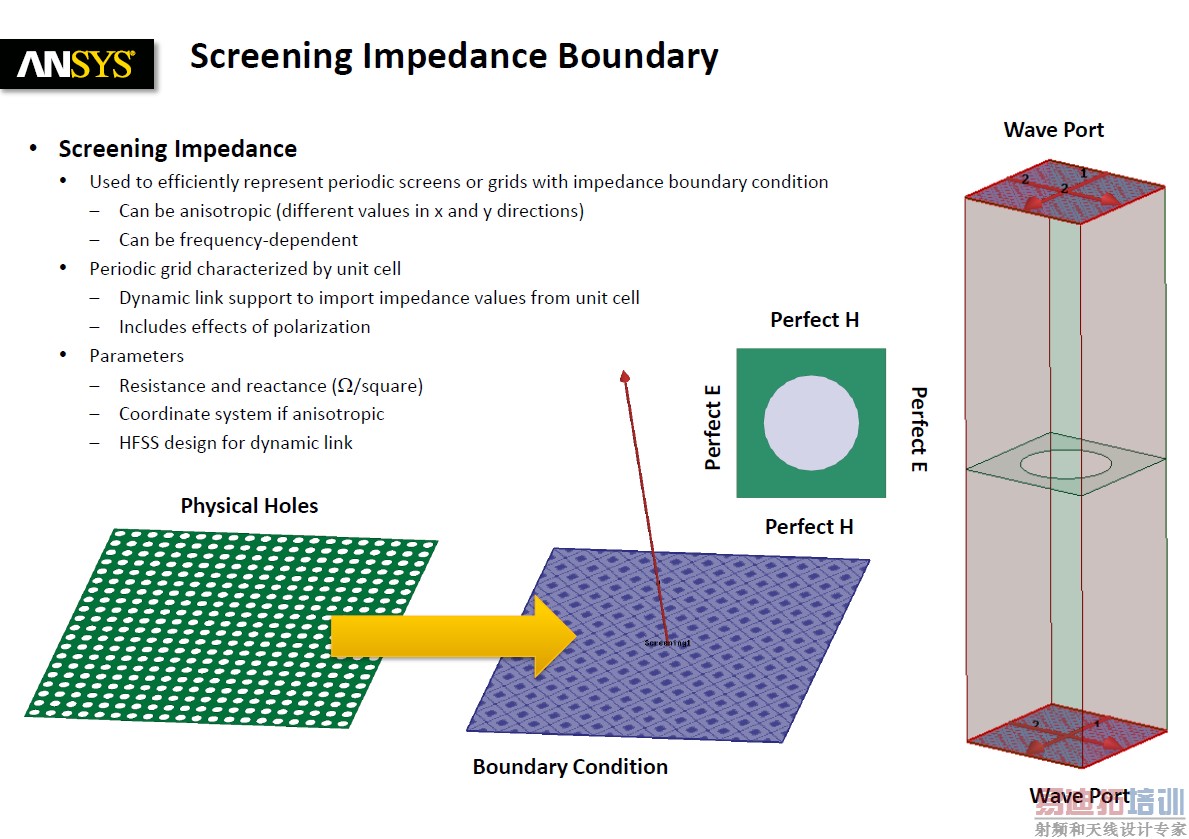
嗯,那你可以开始考虑这个模式了...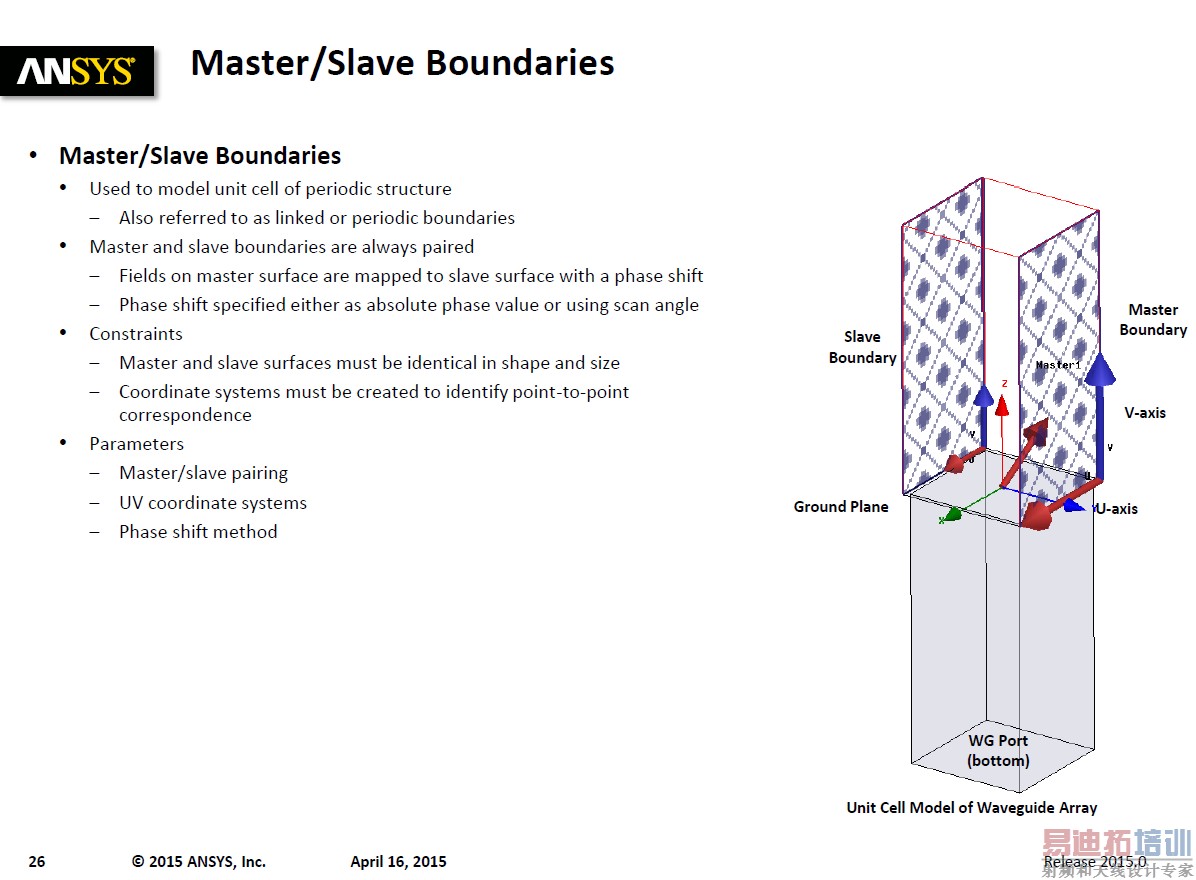
申明:网友回复良莠不齐,仅供参考。如需专业解答,请学习易迪拓培训专家讲授的HFSS视频培训教程。
上一篇:HFSS仿真进度条一直不动了
下一篇:微带贴片八木天线馈电方式


