- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Eigenmode Solver Parameters
 Simulation: Solver
Simulation: Solver 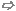 Start Simulation
Start Simulation  Eigenmode Solver
Eigenmode Solver
If you are not familiar with what the eigenmode solver does and what it is used for, you should first read the Solver Overview or the Eigenmode Solver Overview.
The eigenmode solver allows the calculation of resonant modes for loss free structures without open or conduction wall boundary conditions, and structures with electric/magnetic losses provided that the assumption of a frequency independent complex permittivity or reluctivity is valid. Before you start the solver you should have made all necessary solver settings. After the simulation has finished, the calculated modes are listed in the result window. The field patterns can be accessed through the navigation tree in 2D/3D Results  Modes.
Modes.
Solver settings frame
Mesh type: The eigenmode solver offers a hexahedral mesh as well as a tetrahedral mesh for the discretization of the computation domain.
Method: For the hexahedral mesh two different eigenmode solver methods are provided, namely AKS (Advanced Krylov Subspace) and JDM (Jacobi-Davidson Method). Please note, that the latter is capable to handle also electrically or magnetically lossy problems by considering frequency independent complex permittivity or reluctivity values, as discussed in the Eigenmode Solver Overview.
Modes: In this field, you may specify the number of modes to be calculated. The eigenmode solver will always calculate the resonant modes with the lowest frequencies. If the JDM eigenmode solver method is selected you have the possibility either to automatically calculate all modes from the lower frequency to the upper frequency limit by activating the corresponding radio button Choose number of modes automatically (fmin...fmax). This option is designed to ensure that all modes in the given frequency band are found, without the need to subsequently increase the number of modes to calculate. Or you can activate the radio button Frequencies above, which allows you to enter a lower limit to the modes' frequencies. Admissible values are zero to the maximum frequency of the frequency range. The eigenmodes above this frequency are then calculated in ascending order.
Store all result data in cache: Check here if you want the solver results to be stored in the result data cache. The efficient usage of the result data cache is explained in the printed documentation "Advanced Topics".
Q-factor calculation frame
Calculate external Q-factor: If this check button is activated the external Q-factor will be automatically calculated after the eigenmode solver run. This option requires Consider losses in postprocessing only to be active.
Consider losses in postprocessing only: It is common practise for Eigenmode calculations to ignore the losses in a first step, namely for the calculation of the Eigenmode solutions themselves. An approximate consideration of the losses is still possible in the post processing however, by assuming that the losses generated on the boundary can be calculated from the loss-free case. This approach, also referred to as perturbation method, speeds up the calculation.
If Consider losses in postprocessing only is deactivated, the JDM solver with hexahedral mesh and the Eigenmode solver with tetrahedral mesh may consider material losses to some extent, as described above. Q-factors for resonant structures can be calculated directly in that way.
However, by activating this check button the solver is forced to solve the loss-free problem, similar to the Simplify Model settings for the material treatment in the solvers. But using Consider losses in postprocessing only instead of "Simplify Model", the Q-factor can be calculated afterwards by means of perturbation analysis as a post processing step.
Please note that the AKS solver only solves loss-free problems, so that the perturbation analysis is automatically performed to receive Q-factor information. Consequently the check button is disabled for this solver type.
Adaptive mesh refinement frame
Enable: Mark this check box to activate the adaptive mesh refinement. The mesh will be modified by successively changing the settings of the mesh expert system. Press the Properties... button to edit the current settings for the mesh refinement.
Start
Store the specified settings and start the calculation of the resonant modes.
Optimize...
This button brings you into the Optimize dialog box that allows you to set up and start an optimization run.
Parameter Sweep...
This button opens the Parameter Sweep dialog box that allows you to set up and start a sequence of parameterized simulations. Note that it is necessary for the model to contain parameterized structure elements or solver settings.
Acceleration...
Opens the acceleration dialog box to control the high performance options of the simulation run (e.g. GPU acceleration, Distributed Computing, MPI).
Specials...
This button either opens the Eigenmode Solver Specials Dialog (AKS), the Eigenmode Solver Specials (JDM), or the Eigenmode Solver Specials (Tetrahedral). Here you can specify some special settings concerning the eigenmode solver with the selected method.
Simplify Model...
Opens the simplify model dialog.
Apply
Store the specified settings without starting the calculation.
Close
Closes this dialog box without performing any further action.
Help
Shows this help text.
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇:CST2013: Settings for PML Boundary
下一篇:CST2013: Waveguide Port
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B
