- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Port Mode View
To view your port modes, you can use a 2D Vector Plot or a 2D Scalar Plot.
From the navigation tree, select the port mode and component you want to visualize. The entries in the navigation tree depend on the properties of the ports.
General naming conventions of folder entries
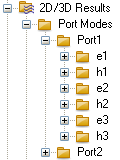
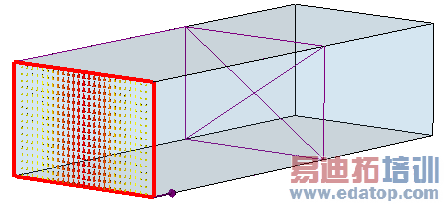
| For every waveguide port you can visualize the electric and magnetic fields as 2D vector plots by clicking on the folder named eM (electric) and hM (magnetic), respectively. M denotes the number of the mode of the waveguide port. The picture on the left shows the folder entries for the electric and magnetic fields of port 2 for the first and second mode. |
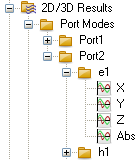
| In addition, you can visualize components of the fields and the magnitude of the fields in a 2D scalar plot. Click on the X,Y or Z entry to visualize the respective field component. To visualize the magnitude of the field, click on the Abs entry. |
Inhomogeneous waveguide ports
| Frequency Domain Solver: If the modelled structure contains inhomogeneous waveguide ports, the electromagnetic fields of the mode are calculated at several frequency samples (for detailed information, see the Waveguide Port Overview page). Time Domain Solver: If the modelled structure contains inhomogeneous waveguide ports, and if either the full deembedding feature or the broadband port is activated, the electromagnetic fields of the mode are calculated at several frequency samples (for detailed information see the Waveguide Port Overview page). To distinguish the fields at the different frequency samples, select the appropriate folder and activate the main view with a mouse click. Now use the page up and page down keys to change the frequency of the mode. |
Single-ended port modes
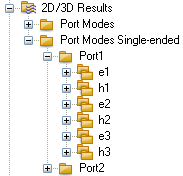
| For single-ended ports the corresponding modes can be accessed via an additional folder showing the single-ended modes. They correspond to the single-ended pin description. |
Evanescent port modes
| In the case of evanescent modes in addition to the port mode, the distance where the mode is damped to -40 dB is displayed, as demonstrated in the picture. |
In the lower left corner the following values are plotted:
Type: E-Field or H-Field
Maximum: In the case of a vector plot, the value of the maximum arrow.
Component: In the case of a scalar plot, this parameter determines which component is plotted.
Mode type: The type of the plotted mode: TEM, Quasi TEM, TE, TM or Unknown
Accuracy: The accuracy of the calculation for the plotted mode.
Fcutoff: In the case of a TE or TM mode, this is the cutoff frequency.
Beta: The mode’s Beta value.
Alpha: In the case of an unknown mode type or TE / TM mode,this is the Alpha value.
Dist.-40 dB: The distance where the field values of an evanescent mode are damped to -40 dB.
Wave Imp.: The wave impedance in Ohms. See Waveguide Port Overview for impedance definitions.
Line Imp.: For mode type TEM or Quasi TEM, this is the line impedance in Ohms. See Waveguide Port Overview for impedance definitions. In case of a complex line impedance, its magnitude is displayed.
Imp. ZPV re/im: This is the impedance in Ohms which is determined by the computed voltage along a line and the mode's complex power. re and im indicate its real and imaginary part. See Waveguide Port Overview for impedance definitions.
Plane at x/y/z: Coordinate of the port plane in the specific orientation (x/y/z).
Frequency: The frequency for which the modes and their parameters have been calculated. This is the center of the frequency range given in Frequency Range Settings.
Phase: The phase for which the mode is plotted.
Maximum-2d: Displays the value and location of the maximum field, depending on the selected type.
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B