- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Sensitivity Analysis Overview
For the frequency domain solver with tetrahedral mesh, for the transient solver with hexahedral mesh as well as for the eigenmode solver with tetrahedral mesh the derivatives of network parameters (S, Y, Z-parameter) with respect to geometric and/or material (simple) design parameters can be calculated without re-meshing the example. With the information of the nominal value and the first derivative the variation of a network parameter with respect to a design parameter can be calculated in a small neighbourhood of the nominal value (see yield analysis overview). Also the sensitivity information is used for a more efficient optimization (see optimizer overview).
How to setup the sensitivity analysis
Before you can start the sensitivity analysis you have to define geometric and/or material design parameters (see Define Face Constraints( ) ).
) ).
Then you may choose the frequency domain or the transient solver, open the solver dialog and activate the Use sensitivity analysis box at the bottom of the dialog:

Press the "Properties..." button to see a complete list of parameters (both available and unavailable parameters for the sensitivity analysis).
Only the available parameters can be selected. Hovering over an unavailable parameter shows why it cannot be used (see the next paragraph about the limitations on parameters):
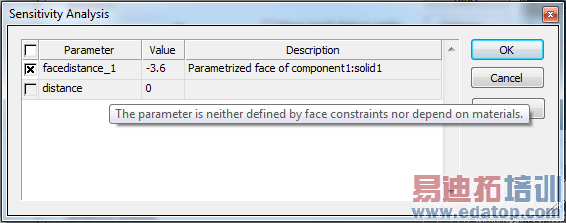
Check those parameters you want to be calculated by the sensitivity analysis and start the solver.
Geometric and material design parameter (sensitivity analysis parameter)
To be able to calculate the sensitivity of network parameters with respect to design parameters, these design parameters have to fullfil some limitations.
Only the following operations are parametrizable by sensitivity parameters:
Defining normal materials with variable Epsilon, Mue, Electric Conductivity or Magnetic Conductivity.
Defining lossy metal material. (only supported by the Frequency Domain Solver)
Defining Face Constraints (variable radius or distances to points or principal planes). (only supported by the Frequency Domain Solver)
In addition, you have to make sure that the parameter
is not used inside any expression.
is not used in any operations not listed above.
If all requirements are met, the parameter will be selectable for sensitivity analysis in the solver dialog (See Solver dialog: Sensitivity analysis).
If you expect a parameter to appear in that list which does not, it may help to check the variable dependencies in the parameter list.
Mechanical displacement (sensitivity analysis parameter)
Displacement field results from the structural mechanics solver can be used to define a local deformation of the structure. The S-parameter sensitivity for the imported displacement field can be calculated in the high frequency solver with tetrahedral mesh. Provided that a mechanics simulation has been performed already, choose Simulation: Sources and Loads  Field Import
Field Import  to browse for the structural mechanics solver's project. See the Coupled Simulation Examples of the structural mechanics solver (Combline Filter) for details.
to browse for the structural mechanics solver's project. See the Coupled Simulation Examples of the structural mechanics solver (Combline Filter) for details.
Postprocessing
The following postprocessing steps can be done for the derivative of S-parameters:
The S-parameter derivatives are renormalized by choosing Post Processing: Signal Post Processing
 S-Parameter Calculations
S-Parameter Calculations 
 Renormalize S-Parameter ...
Renormalize S-Parameter ...The S-parameter derivatives are deembeded by choosing Post Processing: Signal Post Processing
 S-Parameter Calculations
S-Parameter Calculations 
 Deembed S-Parameter ...
Deembed S-Parameter ...The S-parameter derivatives are converted into impedance and admittance parameters sensitivities by choosing Post Processing: Signal Post Processing
 S-Parameter Calculations
S-Parameter Calculations 
 Calculate Z and Y Matrices The Y-,Z-parameter derivatives can be accessed via the 1D Results (S-Parameter Sensitivity, Y-Parameter Sensitivity, Z-Parameter Sensitivity).
Calculate Z and Y Matrices The Y-,Z-parameter derivatives can be accessed via the 1D Results (S-Parameter Sensitivity, Y-Parameter Sensitivity, Z-Parameter Sensitivity).Once the sensitivity information was successfully calculated the yield analysis can be called.
Current restrictions: The sensitivity calculation is done for excited ports only. This also holds for output ports of the S-parameter matrix. Consider a two port system with ports 1 and 2, for instance. Only the sensitivity information for S11 will be calculated if port 1 is excited, but port 2 is not.
Further limitations are design parameter dependent port modes, gyro tropic materials, periodic boundaries and unit cells.
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇:CST2013: Time Domain Solver Settings
下一篇:CST2013: Navigation Tree Overview
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B
