- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Boolean Operations
Probably the most powerful operation to create complex shapes is the combination of simple shapes by boolean operations. These operations allow you to add two or more shapes together, to subtract one or more shapes from another, to insert shapes into others, and to intersect two or more shapes.
While modifying or creating a new shape, the shape may intersect with another shape of the modeled structure. Depending on the material types of the intersecting shapes, it may be necessary to apply a boolean operation to some of the intersecting shapes to subsequently run any solver. If one of the settings in the Modeling: Tools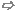 Boolean
Boolean Intersection Check Settings dialog box is checked, an intersection check will be performed automatically if a new shape is being created or modified . In this case, the Shape Intersection Dialog box is launched. You may initiate the Intersection check manually by Modeling: Tools
Intersection Check Settings dialog box is checked, an intersection check will be performed automatically if a new shape is being created or modified . In this case, the Shape Intersection Dialog box is launched. You may initiate the Intersection check manually by Modeling: Tools Boolean
Boolean  Perform Intersection Check
Perform Intersection Check
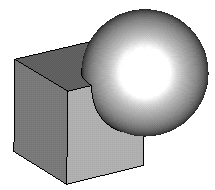
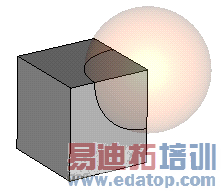
In the following we will consider two shapes—a brick (first shape) and a sphere (second shape) —on which we will perform boolean operations:
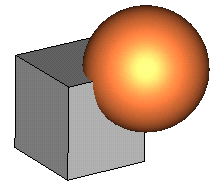
Add brick to sphere: Add both shapes together to obtain one single shape. The resulting shape will get the name and the material of the first shape. |
|
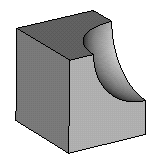
Subtract sphere from brick: Subtract the second shape from the first to obtain one single shape. The resulting shape will get the name and the material of the shape from which the other shape is subtracted. |
|
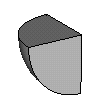
Intersect brick and sphere: Intersect two shapes to form a single shape. The resulting shape will get the name and the material from the first shape of this operation. |
|
Insert sphere into brick (Trim brick): The second shape will be inserted into the first one. Again, both shapes will be kept. The resulting shapes will have no intersecting volume. |
|
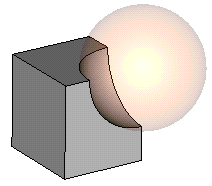
Imprint sphere into brick: The second shape will be imprinted into the first one. Again, both shapes will be kept and the first shape remains unchanged. The faces of the second shape will be split at the intersection curves with the first shape. Subsequent face-pick operations can now independently select each part of the split faces. |
|
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇:CST2013: Curve Properties
下一篇:CST2013: Time Signal Processing / TDR Cross-Probing
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B