- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Structure Editing Overview
The structure definition, as described in the Shape creation overview page, allows the input of structure elements. However, the structures usually need to be edited afterwards. There exist, in general, three different ways to modify existing structures: Editing the History List, Editing the History Tree, and performing Local Operations on the model.
Editing the History List
The History List stores all macro language commands for each creation step.
You may edit the shapes in the History List by just selecting the corresponding line and pressing the Edit button. Afterwards, you may modify the commands directly.
Pressing the Update button in the History List will finally re-generate the modified structure.
Editing the History Tree
A very convenient way to change the shape parameters of existing shapes is to select a shape and choose the Edit  Object Properties from the main menu or Properties from the context menu.
Object Properties from the main menu or Properties from the context menu.
If the selected shape is still a basic shape, the shape creation dialog box for the particular shape type will open automatically and show the shape’s current parameters. You may now edit the parameters and press the OK button to re-generate the structure with the modified shape.
If the edited shape is the result of one or more boolean operations, a so called History Tree window will open. The tree shows the construction history of the selected shape, including the generation of basic shapes, transformations and boolean operations.
You may now select a particular basic shape or transform operation from the History Tree and press the Edit button. Now, either the shape creation dialog box or the transform dialog box will open. You may now edit the parameters and press the OK button to re-generate the structure with the modified parameters.
Local Operations on the Model
Editing the structures with either the History List or the History Tree requires the presence or parametric information. However, for imported models from other CAD systems, this information usually is not available.
On the other hand, sometimes only small modifications are necessary to a shape produced by complex operations. In such cases, it may also become complicated to perform the desired change by altering the elementary shapes.
In cases where some elements of the model need to be modified directly, there are two modes to help to complete this task:
Modeling: Tools
 Modify Locally
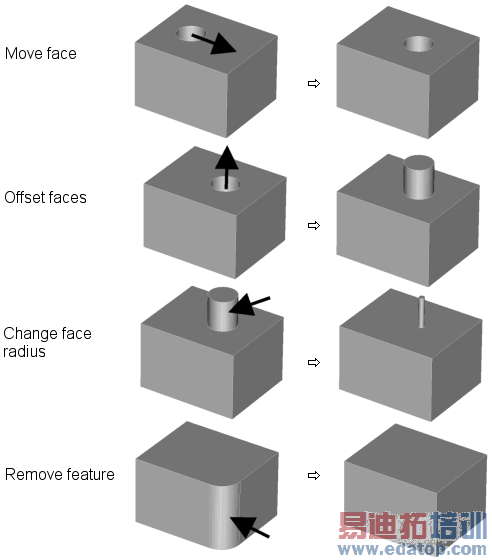
Modify Locally Modify Face: Three operations are offered:
Modify Face: Three operations are offered:Offset face: This operation moves the surface in the normal direction in each point of the selected face
Move face: The selected faces may be moved by a translation vector. This operation will sometimes fail if heavy topology changes occur because of face translation.
Remove feature: Activating this command will prompt the program to attempt to remove the selected faces. The resulting gaps in the model will be automatically closed by extending the neighboring faces. The operation will fail if the model is not closed by face extensions.
Modeling: Tools
 Modify Locally
Modify Locally Define Face Constraints: Even though this feature is designed for defining sensitivity analysis parameter, especially setting the radius of cylindrical faces might be of great help for editing imported models. Three definitions of constraints are offered (see Define Face Constraints for a detailed description):
Define Face Constraints: Even though this feature is designed for defining sensitivity analysis parameter, especially setting the radius of cylindrical faces might be of great help for editing imported models. Three definitions of constraints are offered (see Define Face Constraints for a detailed description):Set distance to plane: A fixed distance between one of the principal planes and the selected faces is defined. Internally this is done by moving the faces.
Set distance to point: A fixed distance between a base point and the selected planar faces is defined. Internally this is done by offsetting the planar faces.
Set radius: Selected cylindrical faces are set to a given radius. Internally this is done by offsetting the faces.
Examples
In addition there are some more operations for applying structural changes to existing shapes:
Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Fill up Surronding Space: This operation creates a new solid that fills the entire calculation volume. You will obtain a new shape in which all shapes defined thus far are completely embedded. In a manner of speaking, this action creates a ”negative form” of your structure.
Fill up Surronding Space: This operation creates a new solid that fills the entire calculation volume. You will obtain a new shape in which all shapes defined thus far are completely embedded. In a manner of speaking, this action creates a ”negative form” of your structure.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Slice by UV Plane: Cuts shapes into two new shapes. The cutting plane is the uv plane defined by the local coordinate system.
Slice by UV Plane: Cuts shapes into two new shapes. The cutting plane is the uv plane defined by the local coordinate system.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Separate Shape: Splits shapes with separate bodies.
Separate Shape: Splits shapes with separate bodies.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Merge Materials of Component: Makes a single shape for each material of the selected component .
Merge Materials of Component: Makes a single shape for each material of the selected component .
Face Healing
There are various editing possibilities concerning faces and curves of a selected shape. A curve represents an edge that does not necessarily belong to any face. For example, sometimes the surface representation of imported shapes may be corrupted such that one of the following operations may be helpful in repairing and further editing the elements.
Clean Shape: (Objects  Solid Healing Tools
Solid Healing Tools Clean Shape) This operation removes all unnecessary faces or edges from the selected shape.
Clean Shape) This operation removes all unnecessary faces or edges from the selected shape.
Face Operations: These operations are used to modify single face elements.
Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Delete Selected Faces: Deletes a selected face.
Delete Selected Faces: Deletes a selected face.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Cover Edges: Fits a surface over a closed loop of curves or edges.
Cover Edges: Fits a surface over a closed loop of curves or edges.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Loft Edges: Creates a face by lofting two edges.
Loft Edges: Creates a face by lofting two edges.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Skin Edges: Fits a surface through a series of curves or edges.
Skin Edges: Fits a surface through a series of curves or edges.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Sweep First Edge Along Second: Creates a planar face as a rhomboid between two adjacent dangling edges.
Sweep First Edge Along Second: Creates a planar face as a rhomboid between two adjacent dangling edges.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Reverse Selected Faces: Inverts the normal orientation of a selected face.
Reverse Selected Faces: Inverts the normal orientation of a selected face.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Reverse Faces of Selected Shape: Inverts the normal orientation of all faces belonging to the selected shape.
Reverse Faces of Selected Shape: Inverts the normal orientation of all faces belonging to the selected shape.Modeling: Shapes
 Faces and Apertures
Faces and Apertures Shape from Picked Faces: This operation creates a solid from the selected faces.
Shape from Picked Faces: This operation creates a solid from the selected faces.
Curve Operations: These operations are used to create curve elements which belong to the selected solids.
Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Add Linear Curve Between two Points: Creates a linear curve between two picked points and adds it to the currently selected shape.
Add Linear Curve Between two Points: Creates a linear curve between two picked points and adds it to the currently selected shape.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Add Tangent Curve: Creates a tangent curve between two points, each belonging to an own edge and stores it within the selected shape.
Add Tangent Curve: Creates a tangent curve between two points, each belonging to an own edge and stores it within the selected shape.Modeling: Tools
 Shape Tools
Shape Tools Healing Tools
Healing Tools Model Healing
Model Healing Split Edge at Point: Splits the selected edge into two parts, determined by the position of the picked point on the edge.
Split Edge at Point: Splits the selected edge into two parts, determined by the position of the picked point on the edge.
Shape Healing
Use the healing operations (Modeling: Tools Shape Tools
Shape Tools Heal Shape) and (Modeling: Tools
Heal Shape) and (Modeling: Tools Shape Tools
Shape Tools Heal All Shapes)) to repair imported shapes.
Heal All Shapes)) to repair imported shapes.
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇:CST2013: PIC Solver Problem Handling
下一篇:CST2013: Arc Creation Mode
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B
