- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
CST2013: Local Mesh Properties (Hexahedral)
 Mesh: Mesh Control
Mesh: Mesh Control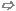 Local Properties
Local Properties
(navigation tree: Groups:Mesh Groups:meshgroup1 Local Mesh Properties)
Local Mesh Properties)
(navigation tree: Components:solid1 Local Mesh Properties)
Local Mesh Properties)
(navigation tree: Wires:wire1 Local Mesh Properties)
Local Mesh Properties)
This dialog allows you to control the mesh properties of one or more selected objects. In case of multiple selected objects (holding down the CTRL key while selecting a shape), the check boxes are in an undefined state such that they are neither checked nor unchecked.
Consider for simulation: Choose whether or not the selected shape should be considered by the calculation.
Consider for bounding box: Choose whether or not the selected shape should be considered for the bounding box calculation.
Both Consider for simulation and Consider for bounding box settings are applied at the object level, and are not part of mesh group settings.
Mesh group
Provide a mesh group name. Mesh groups are used to group objects (i.e. Solids and Wires) together. They hold a set of local mesh properties and these settings are inherited by the objects which are part of the mesh group. If an object is removed from the mesh group, its local mesh properties are reset to default.
Automesh and simulation settings
Mesh type: Choose between the following choices:
Default: The default mesh type is set in the Special Mesh Properties Dialog.
PBA: The most accurate Perfect Boundary Approximation? is recommended.
Staircase mesh: Use the classic finite difference staircase scheme for surface bodies or imported shapes that produce errors during the matrix generation.
Priority: The priority is used for two purposes: material distribution control and mesh line control:
Material distribution control: If the staircase mesh or human model is used, the material with the higher mesh priority overwrites all other materials in each mesh cell.
Mesh line control: The automatic mesh generation will always attempt to avoid extremely small mesh-line distances because this would significantly increase the simulation times. If the mesh generator has created two fixpoints that are very close to each other, by default the mesh lines will be merged and the resulting mesh line will be located between these two fixpoints.
However, it might be desirable to pay more attention to an important structure detail. In these cases, a priority for each shape can be defined.
All shapes will have a priority of zero by default.
Whenever the automatic mesh generator must decide to merge two mesh lines, it will choose the location of the fixpoint from the shape with the higher priority. Only when all fixpoints have the same priority the mesh lines will be merged again.
Automesh fixpoints: Choose whether or not the fixpoints of the selected shape should be considered by the automatic mesh generation.
Consider for refinement: Choose whether or not the selected shape should be considered for the mesh refinement. If unchecked selected shape will not participate in edge, face and material based refinement.
Material based refinement: Choose whether or not the material based refinement should be considered by the mesh generation of the selected shape.
Snapping settings
Consider for snapping: Choose whether or not the selected shape should be considered for snapping.
Intervals in x, y, z: Using this you can generate regularly spaced snapping planes inside shape's bounding box. Let's say you have an axis-aligned cube, and If you define 2 intervals in x, you will get an additional x-snapping plane at the center of the cube.
Mesh refinement settings
Use local edge refinement factor: Increases the refinement around edges of the object by the specified factor.
Use local volume refinement factor: Increases the refinement within the boundary of the object by the specified factor.
Maximum mesh step width settings
Use step width and extend range: Choose whether or not the step width and the extend range should be considered by the mesh generation of the selected shape.
Dx/Dy/Dz: For structure elements of high importance for the simulation a maximum step width for every coordinate direction can be specified. The automatic mesh generator will not exceed this step width at the bounding box of this structure element.
Extend x/y/z range by: Use this setting to extend the maximum step width outside the bounding box of this structure element by the range given.
OK
Accepts the input and closes the dialog.
Apply
Accepts the input without closing the dialog.
Update
Updates the mesh view.
Cancel
Closes this dialog box without performing any further action.
Help
Shows this help text.
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇:CST2013: Edit / Move / Delete Macro
下一篇:CST2013: Edit History List Item
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- CST2013: Mesh Problem Handling
- CST2013: Field Source Overview
- CST2013: Discrete Port Overview
- CST2013: Sources and Boundary C
- CST2013: Multipin Port Overview
- CST2013: Farfield Overview
- CST2013: Waveguide Port
- CST2013: Frequency Domain Solver
- CST2013: Import ODB++ Files
- CST2013: Settings for Floquet B
