- 易迪拓培训,专注于微波、射频、天线设计工程师的培养
Microstrip Line - CST2013 MWS Examples
Hexahedral mesh:
Tetrahedral mesh:
General Description
This example demonstrates an eigenmode calculation with periodic boundaries in z-direction, using the JDM eigenmode solver and the standard tetrahedral solver. The phase shift of the periodic boundary is defined as a parameter which is swept from 5 degrees to 175 degrees with a step size of ten degrees.
A user defined parameter sweep watch monitors the sweep process, thereby creating group velocity, phase velocity and dispersion diagrams.
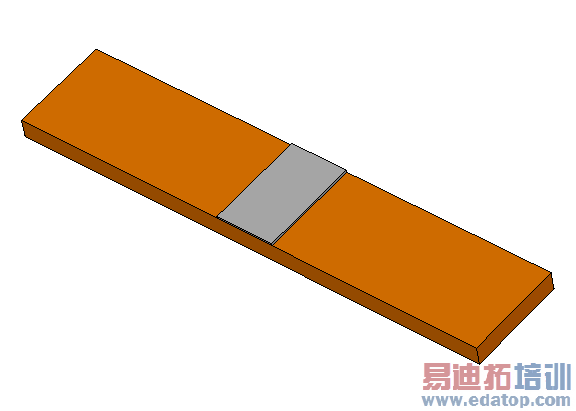
The structure comprises a microstrip line (width = 2.4 mm, height = 100 μm) on a substrate with epsilon_r = 9.
Structure Generation
The background material is defined as vacuum, the units are changed to millimeters, gigahertz and nanoseconds, and the boundary conditions are set to "electric". The two boundary conditions in z-direction are changed to "periodic" in order to model an infinite extent of the microstrip line.
After creating a new layer named "substrate", the substrate is added as a brick shape.
The working coordinate system (WCS) is aligned with the top face of the substrate. Thereafter, the microstrip line is created by adding another box to the "PEC" layer.
The frequency range starts at DC and ends at 15 GHz. The upper distance to the boundary above the substrate is increased by seven millimeters, and a magnetic symmetry condition is specified.
Mesh Settings
The number of steps per wavelength is increased to 7 and the minimum number of steps is increased to 12 for the tetrahedral mesh to obtain accurate results.
Solver Setup
Whenever the eigenmode solver is started, a specific number of the lowest eigenmode frequencies of the structure are calculated. With periodic boundaries and a non-zero phase shift, those eigenmodes are traveling waves. Since only the fundamental mode is of interest, the number of modes is reduced to one. The JDM eigenmode solver is chosen, which is faster for the given example, for the hexahedral mesh.
After the parameter sweep has been selected from the eigenmode solver's dialog, a new sequence is added, and the parameter "phase" is chosen to be swept from 5 to 175 degrees in 18 steps.
A user defined watch is already available and may serve as a template for building custom watches. Please select Edit to view or modify the source code.
Post Processing
The user defined parameter sweep watch adds the group velocity, phase velocity and dispersion plots to the navigation tree in the folder 1D Results.
CST微波工作室培训课程套装,专家讲解,视频教学,帮助您快速学习掌握CST设计应用
上一篇: Rectangular Patch Antenna - CST2013 MWS Examples
下一篇: PEC Sphere - CST2013 MWS Examples
 最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
最全面、最专业的CST微波工作室视频培训课程,可以帮助您从零开始,全面系统学习CST的设计应用【More..】
频道总排行
- Rectangular Waveguide Tutorial
- FSS: Simulation of Resonator
- CST2013 MWS Examples: Thermal C
- Dipole Antenna Array - CST201
- CST MWS Examples - CST2013 M
- Microstrip Radial Stub - CST2
- Dielectric Resonator Antenna -
- Interdigital Capacitor - CST20
- CST2013 MWS Examples: Biological
- Lossy Loaded Waveguide - CST2
